Future of Green Energy
Introduction
Green energy, also known as renewable energy, is energy that is produced from sources that are naturally replenished and do not deplete over time. Examples of green energy sources include solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass. Unlike fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, which are finite and non-renewable, green energy sources provide a sustainable and clean source of energy.
Green energy has become increasingly important in recent years due to concerns about climate change, air pollution, and energy security. Burning fossil fuels releases large amounts of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, which contribute to global warming and other environmental impacts. In contrast, green energy sources produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions, making them a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
In addition to being environmentally friendly, green energy can also provide economic benefits. The transition to green energy can create new job opportunities in industries such as solar panel manufacturing, wind turbine installation, and energy efficiency consulting. Green energy can also reduce dependence on foreign energy sources, increase energy security, and promote economic growth through innovation and technological advancements.
Governments around the world are increasingly investing in green energy and implementing policies to encourage its use. The United Nations has also established a goal of achieving universal access to modern energy services and doubling the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix by 2030, as part of the Sustainable Development Goals.
In conclusion, green energy is an important and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, providing a clean source of energy that can help mitigate the impacts of climate change, reduce air pollution, and promote economic growth. As we face the challenges of the 21st century, transitioning to green energy is essential for a sustainable and prosperous future.
At this time, we rely almost exclusively on fossil fuels to heat and power our houses as well as fuel our vehicles. The usage of coal, oil, and natural gas to fulfil our energy requirements may seem like the most practical option, but there is only a finite amount of these fuels available on the planet.
We are utilising them at a rate that is far faster than they are being produced.
They will, at some point, be exhausted. In addition, the United States is planning to retire a significant portion of its nuclear capacity by the year 2020. This decision was made due to safety concerns as well as issues with waste disposal. In the meanwhile, it is anticipated that the country’s need for energy would increase by 33% over the course of the next 20 years. Renewable sources of energy have the potential to help close the gap. The use of renewable energy sources is preferable for the health of the environment, regardless of whether or not we have an infinite supply of fossil fuels. Renewable energy methods are sometimes referred to as clean or green since they generate very few pollutants if any at all.
However, the combustion of fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, which trap the heat of the sun and contribute to the phenomenon of global warming. The consensus among experts on climate change is that the average temperature of the Earth has increased over the course of the last century. If this pattern continues, there will be an increase in sea levels, and experts estimate that there will be an increase in the frequency of floods, heat waves, droughts, and other types of severe weather events. When fossil fuels are burnt, more contaminants are discharged into the environment, including the air, the soil, and the water. Both individuals and the ecosystem suffer a significant toll at the hands of these contaminants. Diseases such as asthma are made worse by pollution in the air. Plants and fish are both negatively impacted by acid rain, which is caused by sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. Smog is also caused by the presence of nitrogen oxides.
The development of our energy independence as well as our energy security will be facilitated by renewable sources of power. For instance, if we replaced part of our petroleum with fuels generated from plant materials, we might save money and improve our nation’s energy security at the same time.
In addition, it is important to follow the below statement:
Yes, green energy is very important in the near future to help save the environment. The continued use of fossil fuels for energy production has resulted in significant environmental problems such as air and water pollution, climate change, and habitat destruction. Green energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass, have the potential to help reduce or eliminate these problems.
Green energy is important because it is renewable and sustainable. Fossil fuels are finite resources that will eventually run out, while green energy sources can be replenished indefinitely. Green energy is also cleaner than fossil fuels, as it produces fewer emissions and pollutants that harm the environment and human health. By using green energy, we can reduce our carbon footprint and slow down the process of climate change.
The near future is critical for the transition to green energy, as the world’s population continues to grow and the demand energy increases. It is estimated that the world’s energy demand will increase by 50% by 2050. Without a transition to green energy, this increased demand will only exacerbate the environmental problems associated with fossil fuels.
In addition, green energy can have other positive impacts beyond environmental protection. The development of green energy technologies can create new jobs and economic opportunities, particularly in areas such as research, manufacturing, and installation. It can also increase energy independence and reduce reliance on imported fuels, enhancing national security.
In conclusion, green energy is very important in the near future to help save the environment and address the challenges associated with fossil fuels. It is renewable, sustainable, and cleaner than fossil fuels, and its adoption can have positive economic, social, and environmental impacts.
Green energy is crucial for the near future to save the environment and mitigate the impacts of climate change. The burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas releases large amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, leading to global warming, sea level rise, and other environmental impacts. The following are some reasons why green energy is important in the near future to save the environment.
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions: Green energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower do not produce greenhouse gas emissions, making them a clean and sustainable source of energy. In contrast, burning fossil fuels releases large amounts of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change. By transitioning to green energy, we can significantly reduce our greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
- Promoting sustainable development: Green energy sources are renewable and do not deplete over time, making them a sustainable source of energy. Unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and subject to price fluctuations and geopolitical instability, green energy sources can provide a reliable and stable source of energy for future generations. By investing in green energy, we can promote sustainable development and ensure a secure and reliable source of energy for the future.
- Improving air quality: Burning fossil fuels releases harmful pollutants into the air, leading to poor air quality and health problems such as respiratory illnesses, heart disease, and stroke. In contrast, green energy sources do not produce harmful pollutants, improving air quality and promoting public health.
- Creating new job opportunities: The transition to green energy will create new job opportunities in industries such as solar panel manufacturing, wind turbine installation, and energy efficiency consulting. These jobs will help stimulate economic growth and provide opportunities for workers in the renewable energy sector.
- Increasing energy security: By diversifying our energy sources and reducing our dependence on fossil fuels, we can increase our energy security and reduce our vulnerability to price fluctuations and geopolitical instability. Green energy sources are often located domestically, reducing our reliance on foreign energy sources and improving our energy independence.
- Mitigating the impacts of climate change: Climate change is already having significant impacts on the environment and human societies, including sea level rise, increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, and ecosystem disruptions. By transitioning to green energy, we can reduce our greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change, helping to protect our environment and the communities that depend on it.
- Encouraging innovation: The transition to green energy will require significant innovation in energy storage, transmission, and distribution technologies. By investing in green energy, we can encourage innovation and create new opportunities for technological advancement, driving progress and economic growth.
- Supporting international cooperation: The transition to green energy will require international cooperation and collaboration, as many countries will need to work together to develop and implement sustainable energy policies. By promoting green energy, we can support international cooperation and work towards a shared goal of mitigating the impacts of climate change and promoting sustainable development.
In conclusion, green energy is essential for the near future to save the environment and mitigate the impacts of climate change. By transitioning to green energy, we can reduce our greenhouse gas emissions, promote sustainable development, improve air quality, create new job opportunities, increase energy security, mitigate the impacts of climate change, encourage innovation, and support international cooperation. It is essential that we act now to invest in green energy and work towards a sustainable and low-carbon future.

How Green Energy is Working?
As a source of energy, green energy often comes from renewable energy technologies such as solar energy, wind power, geothermal energy, biomass and hydroelectric power. Each of these technologies works in different ways, whether that is by taking power from the sun, as with solar panels, or using wind turbines or the flow of water to generate energy.
Green energy, also known as renewable energy, is produced from sources that are naturally replenished and do not deplete over time. There are several types of green energy sources, including solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass, and each works differently to produce energy.
Solar Energy: Solar energy is produced by converting the sun’s energy into electricity. This is done using solar panels, which are made up of photovoltaic cells that convert sunlight into electricity. The panels are typically installed on rooftops or in large solar farms, and the electricity they produce can be used to power homes and businesses. Solar energy is a clean and sustainable source of energy, as it produces no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants.
Wind Energy: Wind energy is produced by harnessing the power of the wind to turn turbines and generate electricity. This is done using wind turbines, which are tall structures with large blades that spin in the wind. The spinning blades turn a generator, which produces electricity. Wind turbines can be installed on land or offshore, and wind energy is a clean and renewable source of energy that produces no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants.
Hydro Energy: Hydro energy is produced by using the power of moving water to turn turbines and generate electricity. This is done using hydroelectric power plants, which are typically located near dams or other areas where water flows at high speeds. The moving water turns turbines, which generate electricity. Hydro energy is a clean and renewable source of energy, but can have negative impacts on aquatic ecosystems and require significant infrastructure.
Geothermal Energy: Geothermal energy is produced by tapping into the heat of the earth’s crust to generate electricity. This is done using geothermal power plants, which are typically located in areas with high levels of geothermal activity, such as near volcanoes or hot springs. Geothermal energy is a clean and sustainable source of energy, as it produces no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants, but can be expensive to develop.
Biomass Energy: Biomass energy is produced by burning organic material such as wood, agricultural waste, or other plant matter to generate electricity. This is done using biomass power plants, which can be located in areas with abundant sources of biomass. Biomass energy is a renewable source of energy, but can produce air pollutants and greenhouse gas emissions if not managed properly.
In addition to producing energy, green energy sources can also store and distribute energy. Energy storage is important for ensuring a reliable and consistent source of energy, as green energy sources can be intermittent, producing energy only when the sun is shining or the wind is blowing. Energy storage technologies such as batteries, pumped hydro, and thermal storage can be used to store excess energy produced by green energy sources, which can be used later when energy demand is high.
Green energy sources can also be connected to a grid system, which allows energy to be distributed to homes and businesses. Smart grid technologies can be used to manage energy distribution and consumption, ensuring a more efficient and reliable source of energy.
In conclusion, green energy is produced by harnessing the power of natural and renewable sources such as solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass. Each type of green energy source works differently to produce energy, but all are sustainable, clean, and produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants. Energy storage and distribution technologies such as batteries, pumped hydro, and smart grids are used to ensure a reliable and consistent source of energy. As we work towards a more sustainable and low-carbon future, green energy will play an increasingly important role in meeting our energy needs.
What Does it Mean?
A resource cannot be considered a source of green energy if it contributes to the creation of pollution, as is the case with fossil fuels. This indicates that the renewable energy business does not always make use of environmentally friendly sources. For instance, the production of electricity by the combustion of organic material derived from well-managed forests may be a renewable source of energy, but this does not guarantee that it is environmentally friendly since the combustion process itself generates carbon dioxide.
Green energy, also known as renewable energy, is energy that is produced from sources that are naturally replenished and do not deplete over time. These sources include solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass energy. Unlike traditional sources of energy, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, which are finite and contribute to climate change, green energy sources are sustainable and emit little to no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants. Green energy is becoming increasingly important as we work towards a more sustainable and low-carbon future.
In contrast to fossil fuel sources such as natural gas or coal, which may take millions or even billions of years to generate, green energy sources are often renewed via natural processes. Mining and drilling activities are often avoided by green sources because of the potential damage they do to eco-systems.
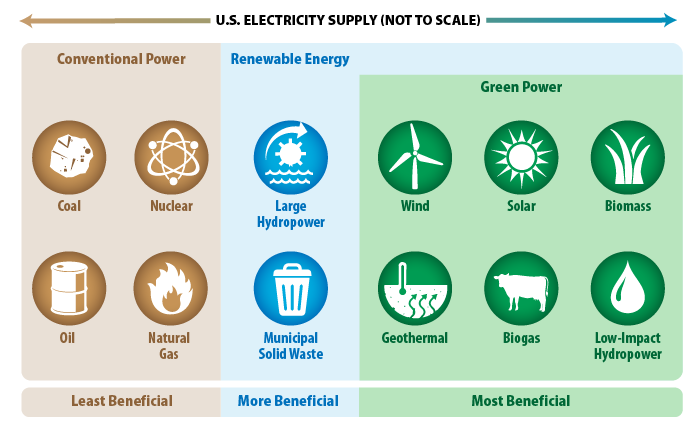
Types of Green Energy
The three primary types of energy are wind power, solar power, and hydroelectric power (including tidal energy, which uses ocean energy from the tides in the sea). Solar and wind power may be created on a domestic scale in people’s homes, or they can be generated on a larger scale in industrial settings. Either way, they can be used to generate electricity.
The six most common forms are as follows:
1. Solar Power
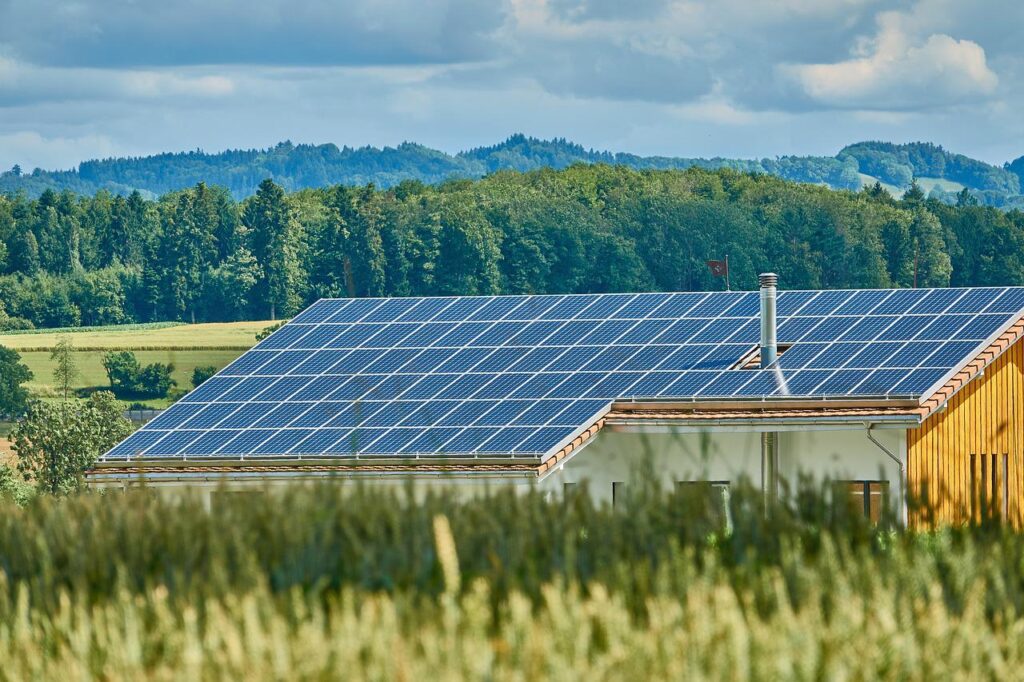
This kind of renewable, eco-friendly energy is often generated using photovoltaic cells, which are designed to soak up light from the sun and convert it into electrical current. In addition to being utilised for lighting and cooking, solar energy may also be used to heat buildings and provide hot water. Solar energy has decreased in price to the point that it is now practical for use in residential applications such as the illumination of gardens, but it is also used on a bigger scale to power whole neighbourhoods.

2. Wind Power
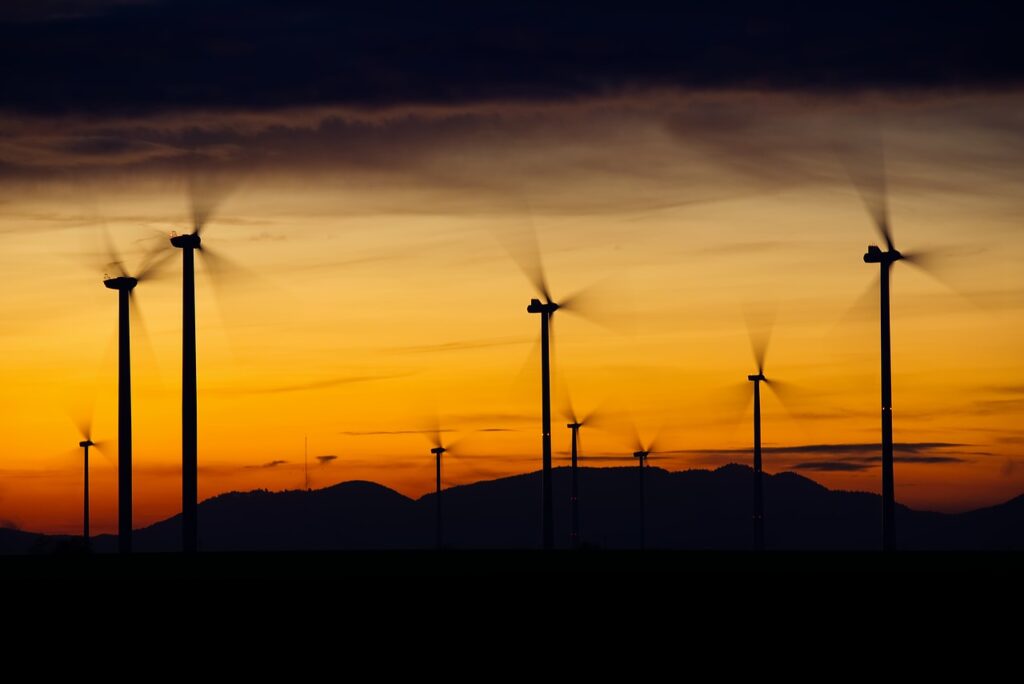
Wind energy harnesses the strength of the movement of air around the planet to turn turbines, which in turn generate electricity. This kind of energy is best used in locations that are offshore or at higher elevations.

3. Hydropower
This sort of environmentally friendly energy is also known as hydroelectric power, and it generates electricity by harnessing the flow of water in rivers, streams, dams, or other locations. The flow of water through pipes in a house may be used to generate hydropower, as can evaporation, rainfall, or the movement of the tides in seas. Hydropower can even be used on a very small scale.

4. Geothermal Energy
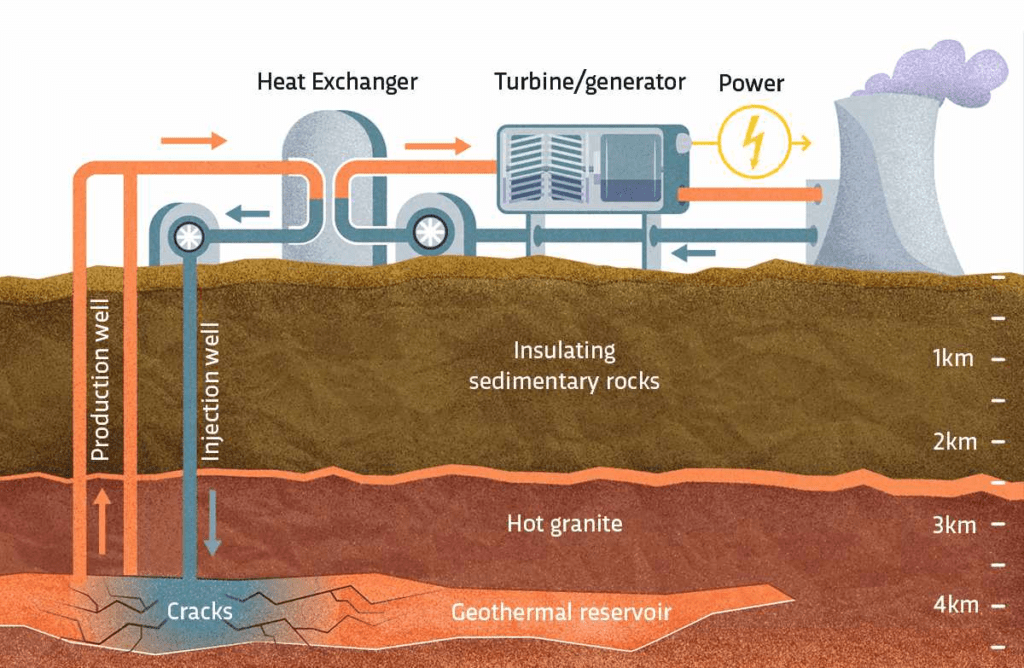
The thermal energy that has been stored just beneath the surface of the ground is used by this kind of environmentally friendly electricity. Even though accessing this resource takes drilling, which raises concerns about its potential effect on the environment, once it is exploited, the resource has enormous potential. Geothermal energy has been utilised for bathing in hot springs for thousands of years. Today, this same resource may be exploited to create steam that turns turbines, which in turn generates electricity. Just the energy that is stored beneath the United States is sufficient to generate ten times the amount of power that can be produced by coal at the moment. It is true that certain countries, like Iceland, have geothermal resources that are simple to reach. However, the use of this resource is highly dependent on its location, and in order for it to be considered really “green,” the drilling processes need to be carefully regulated.
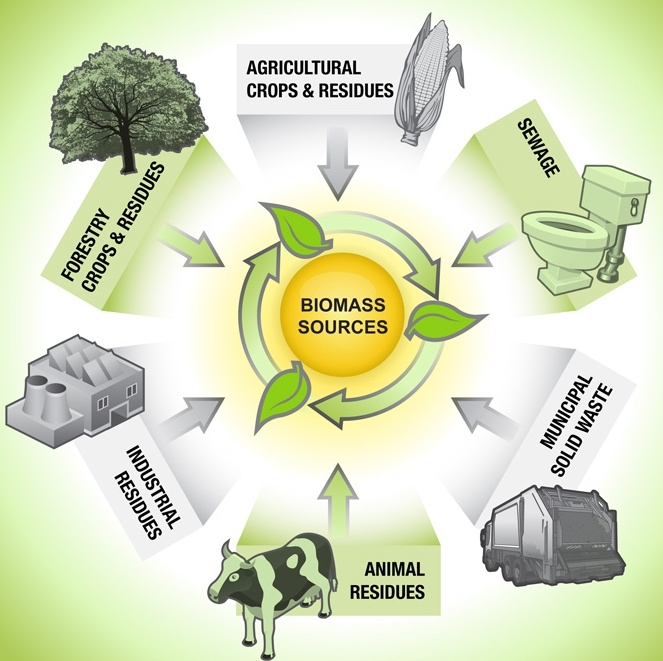
5. Biomass
In order for this renewable resource to be accurately referred to as a source of “green energy,” it is also necessary for it to be properly controlled. In order to generate electricity, biomass power plants burn waste materials such as wood scraps, sawdust, and flammable organic agricultural byproducts. Even though these materials emit greenhouse gases when burned, the levels of these emissions are still far lower than those produced by fuels based on petroleum.
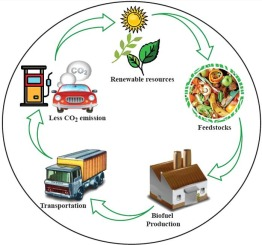
6. Biofuels
These organic materials have the potential to be converted into fuels such as ethanol and biodiesel, as opposed to being burned as biomass as was described before. It is anticipated that biofuels will be able to provide more than 25 per cent of the world’s demand for transportation fuel by the year 2050, despite the fact that they only provided 2.7 per cent of the world’s total fuel for transportation in 2010.