Wind Energy and their advantage, disadvantage & Future Prospects
Introduction
Wind energy is a form of renewable energy that harnesses the power of the wind to generate electricity. It is a sustainable and clean source of energy that does not produce harmful greenhouse gases or other pollutants that contribute to climate change. In this essay, we will explore the history and technology of wind energy, its advantages and disadvantages, and its future prospects.
The history of wind energy dates back to ancient times when people used windmills to grind grain, pump water, and power other machines. In the 19th century, windmills were widely used in rural areas to produce mechanical energy, but it was not until the 20th century that wind turbines were developed to generate electricity. The first wind turbine to produce electricity was built in Scotland in 1887, but it was not until the 1970s that wind energy became a viable source of electricity on a large scale.
Wind turbines work by converting the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical energy that is used to rotate a generator, which then converts the mechanical energy into electricity. There are two main types of wind turbines: horizontal axis turbines and vertical axis turbines. Horizontal-axis turbines have blades that rotate around a horizontal axis, while vertical-axis turbines have blades that rotate around a vertical axis. Horizontal axis turbines are the most common type of wind turbine and are used for large-scale electricity generation, while vertical axis turbines are used for small-scale applications such as powering individual homes or buildings.

The advantages of wind energy are numerous. First and foremost, it is a clean and renewable source of energy that does not produce harmful greenhouse gases or other pollutants. This makes it an ideal alternative to fossil fuels, which are the primary source of greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to climate change. Wind energy is also abundant and widely available, with wind resources located all around the world. This means that wind energy can be used to provide electricity to areas that do not have access to traditional power grids. Additionally, wind energy is cost-effective, with the cost of electricity from wind turbines continuing to decrease as technology improves and economies of scale are achieved.
However, wind energy also has some disadvantages. One of the main disadvantages is that wind is an intermittent source of energy, meaning that it is not always available when needed. Wind speeds can vary widely depending on weather conditions, and wind turbines require a minimum wind speed to generate electricity. This means that wind energy needs to be complemented by other sources of energy such as fossil fuels, hydroelectricity, or solar power to ensure a consistent supply of electricity. Wind turbines can also be noisy and can pose a risk to birds and bats if they are located in areas with high bird or bat populations.
Despite its limitations, wind energy has a bright future. According to the International Energy Agency, wind energy is expected to become the world’s largest source of electricity generation in the next decade, surpassing coal and natural gas. This is due to the rapid growth of wind power installations around the world, as well as advances in wind turbine technology that have made wind energy more efficient and cost-effective. Additionally, the development of energy storage technologies such as batteries and pumped hydro storage will enable wind energy to provide a more reliable and consistent supply of electricity in the future.
In conclusion, wind energy is a clean, renewable, and cost-effective source of electricity that has the potential to play a major role in addressing the world’s energy needs while reducing greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants. While it has some limitations, these can be mitigated with complementary energy sources and technological advancements. As the world continues to transition to a low-carbon economy, wind energy is likely to become an increasingly important part of the energy mix.
Basic of wind energy
Wind energy is a form of renewable energy that harnesses the power of the wind to generate electricity. It is a sustainable and clean source of energy that does not produce harmful greenhouse gases or other pollutants that contribute to climate change.
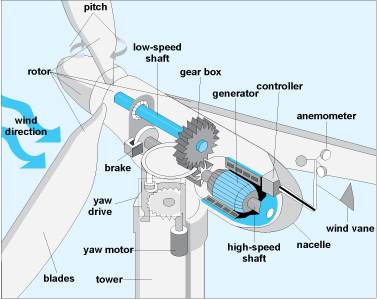
The basics of wind energy involve three key components: the wind turbine, the tower, and the rotor blades. The wind turbine is the device that converts the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical energy. The tower is the tall structure that supports the wind turbine and lifts it high into the air where the wind is stronger and more consistent. The rotor blades are the long, narrow blades that spin around the wind turbine and capture the wind’s energy.
There are two main types of wind turbines: horizontal axis turbines and vertical axis turbines. Horizontal-axis turbines have blades that rotate around a horizontal axis, while vertical-axis turbines have blades that rotate around a vertical axis. Horizontal axis turbines are the most common type of wind turbine and are used for large-scale electricity generation, while vertical axis turbines are used for small-scale applications such as powering individual homes or buildings.
Wind turbines are designed to capture as much wind energy as possible. The rotor blades are aerodynamically designed to capture the maximum amount of energy from the wind, while the tower is tall enough to lift the wind turbine high into the air where the wind is stronger and more consistent. The wind turbine is also equipped with a control system that adjusts the rotor blades to optimize the amount of energy captured from the wind.
Wind energy has several advantages over traditional fossil fuels. First and foremost, it is a clean and renewable source of energy that does not produce harmful greenhouse gases or other pollutants. This makes it an ideal alternative to fossil fuels, which are the primary source of greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to climate change. Wind energy is also abundant and widely available, with wind resources located all around the world. This means that wind energy can be used to provide electricity to areas that do not have access to traditional power grids. Additionally, wind energy is cost-effective, with the cost of electricity from wind turbines continuing to decrease as technology improves and economies of scale are achieved.
However, wind energy also has some limitations. One of the main disadvantages is that wind is an intermittent source of energy, meaning that it is not always available when needed. Wind speeds can vary widely depending on weather conditions, and wind turbines require a minimum wind speed to generate electricity. This means that wind energy needs to be complemented by other sources of energy such as fossil fuels, hydroelectricity, or solar power to ensure a consistent supply of electricity. Wind turbines can also be noisy and can pose a risk to birds and bats if they are located in areas with high bird or bat populations.
In summary, wind energy is a sustainable and clean source of energy that harnesses the power of the wind to generate electricity. It has several advantages over traditional fossil fuels, including its abundance, cost-effectiveness, and lack of harmful emissions. However, it also has some limitations, including its intermittent nature and potential impact on wildlife. Despite these limitations, wind energy is expected to play an increasingly important role in the world’s energy mix as the world transitions to a low-carbon economy.
Reference:
D. Infield and L. Freris, Renewable Energy in Power Systems, 2nd ed., Wiley, 2020
T. M. Letcher, Wind Energy Engineering: A Handbook for Onshore and Offshore Wind Turbines, Academic Press, 2017
V. Nelson and K. Starcher, Wind Energy: Renewable Energy and the Environment, 3rd ed., CRC Press, 2019
J. Wang et al., A review of Danish integrated multi-energy system flexibility options for high wind power penetration, Clean Energy, 1:23–35, 2017
Advantages of Wind Energy
Wind energy has several advantages over traditional fossil fuels and other sources of energy. These advantages include:
- Renewable and Sustainable: Wind energy is a renewable and sustainable source of energy that does not produce greenhouse gas emissions or other pollutants that contribute to climate change. Unlike fossil fuels, wind energy is abundant and widely available, and will never run out.
- Cost-Effective: Wind energy is becoming increasingly cost-effective as technology improves and economies of scale are achieved. The cost of electricity from wind turbines has decreased significantly in recent years, making it a competitive alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
- Job Creation: The wind energy industry creates jobs in the manufacturing, installation, operation, and maintenance of wind turbines. These jobs can provide economic benefits to local communities and contribute to the growth of the green economy.
- Energy Security: Wind energy can help reduce dependence on fossil fuels and foreign oil imports, increasing energy security and reducing the risk of price fluctuations and supply disruptions.
- Abundance and Widely Available: Wind resources are widely available and can be harnessed in many different regions around the world. This means that wind energy can be used to provide electricity to remote areas and communities that do not have access to traditional power grids.
- Low Operational Costs: Once a wind turbine is installed, the operational costs of wind energy are relatively low. The wind is a free resource, and wind turbines require minimal maintenance and upkeep.
- Space-Saving: Wind turbines can be installed on relatively small plots of land, allowing for more efficient use of space compared to other sources of energy.
- Minimal Water Consumption: Unlike traditional fossil fuel power plants, wind energy does not require water for cooling, which can help reduce water consumption and protect water resources.
Overall, wind energy has numerous advantages that make it an attractive alternative to traditional fossil fuels and other sources of energy. As technology continues to improve and economies of scale are achieved, wind energy is expected to play an increasingly important role in the world’s energy mix.
Disadvantages of Wind Energy
While wind energy has several advantages, it also has some disadvantages that should be considered. These disadvantages include:
- Intermittency: Wind energy is an intermittent source of energy because wind speeds can vary widely depending on weather conditions. This means that wind turbines may not always be able to produce electricity when it is needed, which can require the use of backup power sources to ensure a consistent supply of electricity.
- Visual Impact: Wind turbines can be large and visible structures that some people may find unattractive. This can lead to opposition to wind energy projects in some communities, particularly in areas with high levels of tourism or scenic beauty.
- Noise Pollution: Wind turbines can produce noise that can be a source of annoyance or disturbance for nearby residents. While newer wind turbines are designed to be quieter, noise pollution can still be a concern in some locations.
- Potential for Wildlife Impacts: Wind turbines can pose a risk to birds and bats if they are located in areas with high bird or bat populations. This can lead to concern over the impact of wind energy on wildlife, particularly if wind turbines are located in important wildlife habitats.
- Land Use Concerns: Wind turbines require a significant amount of land to be installed, which can lead to concerns over land use and impacts on agriculture or other land uses. This can also lead to opposition to wind energy projects in some communities.
- Initial Investment Costs: While wind energy is becoming increasingly cost-effective, there can be high initial investment costs associated with installing wind turbines. This can make it difficult for some communities or individuals to finance wind energy projects.
- Impact on Radar Systems: Wind turbines can interfere with radar systems used for air traffic control or military operations. This can lead to opposition to wind energy projects in areas where radar systems are important.
Overall, while wind energy has several advantages, it also has some disadvantages that should be considered when evaluating its potential as a source of energy. Despite these limitations, wind energy is expected to play an increasingly important role in the world’s energy mix as the world transitions to a low-carbon economy.
Future Prospect of Wind Energy
The future of wind energy looks promising as the world moves towards a low-carbon economy and seeks to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Here are some of the key prospects for wind energy in the future:
- Continued Growth: Wind energy is one of the fastest-growing sources of renewable energy in the world, and this trend is expected to continue. According to the International Energy Agency, wind energy is expected to grow by 60% by 2024, driven by falling costs and supportive government policies.
- Offshore Wind Energy: Offshore wind energy is becoming increasingly popular as the technology improves and costs decrease. Offshore wind turbines can produce more electricity than onshore turbines due to higher wind speeds and are less visible, addressing some of the concerns associated with onshore wind energy.
- Hybrid Energy Systems: Wind energy is often used in combination with other renewable energy sources, such as solar or hydroelectric power, to create hybrid energy systems. These systems can provide a more stable and reliable source of electricity by leveraging the strengths of different renewable energy sources.
- Smart Grids: Smart grids are becoming increasingly important as the world seeks to integrate more renewable energy sources into the electricity grid. Wind energy can be integrated into smart grids to help balance electricity supply and demand and improve the stability and reliability of the grid.
- Energy Storage: Energy storage technologies, such as batteries and pumped hydro storage, are becoming increasingly important as the world seeks to integrate more intermittent renewable energy sources like wind energy into the electricity grid. Energy storage can help to smooth out fluctuations in electricity supply and demand, improving the reliability of wind energy.
- Floating Wind Turbines: Floating wind turbines are still in the experimental phase, but they have the potential to dramatically expand the areas where wind energy can be harnessed, particularly in deep waters off the coast of countries with limited onshore wind resources.
Overall, wind energy is expected to play an increasingly important role in the world’s energy mix in the coming years and decades, as countries seek to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and transition to a low-carbon economy. With continued technological advancements and supportive government policies, the future of wind energy looks bright.
List of top 10 books on Wind Energy
- “Wind Energy: Renewable Energy and the Environment” by Vaughn Nelson
- “Wind Energy Basics: A Guide to Home- and Community-Scale Wind-Energy Systems” by Paul Gipe
- “Wind Energy Handbook” by Tony Burton, David Sharpe, Nick Jenkins, and Ervin Bossanyi
- “Wind Energy Explained: Theory, Design and Application” by J.F. Manwell, J.G. McGowan, and A.L. Rogers
- “Wind Energy Engineering” by Pramod Jain
- “Wind Energy Generation: Modelling and Control” by Olimpo Anaya-Lara and Nick Jenkins
- “Wind Power for the World: The Rise of Modern Wind Energy” by Preben Maegaard, Anna Krenz, and Wolfgang Palz
- “Offshore Wind Energy Technology” by John O. Tande
- “Wind Energy Conversion Systems: Technology and Trends” by Yong-Hua Song and Allan T. Kirkpatrick
- “The Future of Wind Power” by Bent Sørensen

