Methane Gas
Introduction
Methane gas is a colorless, odorless gas that is the primary component of natural gas. It is a potent greenhouse gas, but it can also be used as a clean and efficient energy storage medium. This is because methane is a hydrocarbon fuel that can be burned to release energy in the form of heat and electricity. Methane has several advantages as an energy storage medium, including its high energy density, ease of transport, and compatibility with existing energy infrastructure. In this article, we will explore the use of methane as an energy storage medium in more detail.
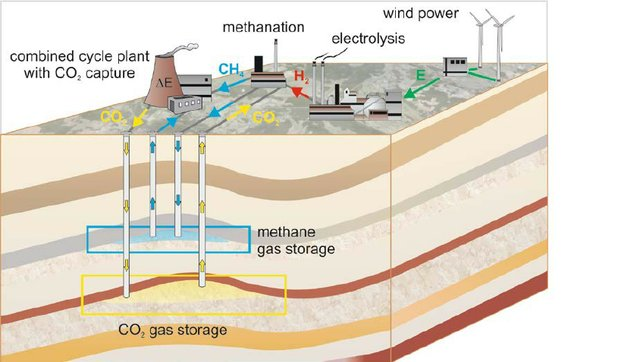
Energy Storage Basics:
Energy storage is the process of capturing and storing energy for later use. Energy storage systems are critical for integrating intermittent renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, into the electric grid. These renewable energy sources produce energy only when the wind is blowing or the sun is shining, so energy storage is needed to store excess energy for use when the wind is not blowing or the sun is not shining.
There are several types of energy storage systems, including batteries, flywheels, pumped hydro, and thermal storage. Methane can be used as a form of thermal storage, which means it stores energy in the form of heat. This is done by burning methane to produce heat, which can then be used to generate electricity or provide space heating.
Methane as Energy Storage:
Methane has several advantages as an energy storage medium. First, it has a high energy density, which means it can store a large amount of energy in a small volume. Methane has an energy density of around 55.5 megajoules per kilogram, which is higher than many other energy storage media, such as batteries and pumped hydro.
Second, methane is a gas, which means it can be easily transported and stored. Methane can be compressed or liquefied for transport, making it easy to transport over long distances. This is important because renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, are often located far away from where the energy is needed.
Third, methane is compatible with existing energy infrastructure. Natural gas pipelines, power plants, and industrial processes are already set up to use methane as a fuel, which means there is no need to build new infrastructure to use methane as an energy storage medium.
Methane can be stored in several ways, including compressed natural gas (CNG), liquefied natural gas (LNG), and underground storage. CNG involves compressing methane to a pressure of around 200 to 250 bar and storing it in high-pressure containers. LNG involves cooling methane to a temperature of around -162°C, which causes it to liquefy and storing it in insulated containers. Underground storage involves injecting methane into underground storage reservoirs, such as depleted gas fields, salt caverns, or aquifers.
Using Methane for Energy Storage:
There are several ways to use methane as an energy storage medium. One way is to use it for electricity generation. Methane can be burned in a gas turbine or a combined cycle power plant to generate electricity. Gas turbines are simple cycle machines that burn natural gas to produce hot gas that drives a turbine, which generates electricity. Combined cycle power plants are more efficient because they use the waste heat from the gas turbine to generate steam, which drives a steam turbine to generate more electricity.
Another way to use methane for energy storage is to use it for space heating. Methane can be burned in a furnace or boiler to produce hot air or hot water, which can be used to heat buildings. Methane can also be used for industrial processes that require high temperatures, such as glass manufacturing or steel production.
Methane can also be used for transportation. Natural gas vehicles (NGVs) are vehicles that run on compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquid.
Benefits of Methane gas as Energy Storage:
Methane gas has several benefits as an energy storage medium, including:
- High Energy Density: Methane has a high energy density, which means it can store a lot of energy in a small volume. This makes it an excellent option for storing energy in a compact and efficient way. It also means that methane can be transported easily over long distances, which is particularly useful for locations that are far away from energy sources.
- Ease of Transport: Methane gas is a gas, which makes it easy to transport over long distances. It can be compressed or liquefied for transport, which makes it easy to move large quantities of methane from one location to another. This is particularly useful for remote locations that are far away from energy sources.
- Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure: Methane gas is already used extensively in the energy sector, particularly for electricity generation and heating. This means that there is already existing infrastructure in place that can be used to store and transport methane gas. This makes it a cost-effective and efficient option for storing energy.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Although methane is a potent greenhouse gas, it can be used as a cleaner alternative to other fossil fuels. When methane is burned, it produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions than other fossil fuels, such as coal and oil. Methane can also be produced from renewable sources, such as agricultural waste, which makes it a renewable energy source.
- Versatility: Methane gas can be used for a variety of purposes, including electricity generation, heating, and transportation. This makes it a versatile energy storage option that can be used in a wide range of applications.
- Lower Cost: Methane gas is often less expensive than other forms of energy storage, such as batteries. This makes it a more cost-effective option for storing energy, particularly for large-scale applications.
Overall, methane gas has several benefits as an energy storage medium. Its high energy density, ease of transport, compatibility with existing infrastructure, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, versatility, and lower cost make it an attractive option for storing energy. As the world transitions to a cleaner energy future, methane gas is likely to play an increasingly important role in energy storage and generation.
Limitation of Methane gas as Energy Storage:
While methane gas has several benefits as an energy storage medium, there are also some limitations to consider:
- Safety Concerns: Methane gas is highly flammable and can be dangerous if not handled properly. There is a risk of leaks or explosions, which can cause harm to people and the environment. Specialized equipment and procedures are required to store, transport, and use methane gas safely.
- Limited Storage Time: Methane gas has a limited storage time, which means it needs to be used or processed within a certain timeframe. If it is stored for too long, it can degrade or lose its energy content, which reduces its effectiveness as an energy storage medium.
- Limited Availability: Although methane gas is widely available, it is not as abundant as other forms of energy, such as coal or oil. Methane gas must be extracted from natural gas fields or produced through renewable sources, such as biogas or biomass. The availability of methane gas can also be affected by geopolitical factors or price fluctuations.
- Environmental Concerns: Although methane gas can be produced from renewable sources, such as agricultural waste or sewage, it is often associated with negative environmental impacts. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change, and its extraction or production can lead to air and water pollution.
- Infrastructure Requirements: While methane gas can be stored and transported using existing infrastructure, it still requires specialized equipment and facilities to be built and maintained. This can be expensive and time-consuming, particularly for large-scale applications.
- Efficiency Losses: There are efficiency losses associated with converting methane gas back into electricity or other forms of energy. These losses can reduce the overall efficiency of the energy storage system and increase the cost of energy production.
Overall, while methane gas has several benefits as an energy storage medium, it is important to consider its limitations and potential drawbacks. Safety concerns, limited storage time, limited availability, environmental concerns, infrastructure requirements, and efficiency losses are all factors that need to be taken into account when evaluating methane gas as an energy storage option.
Future opportunities of Methane gas as Energy Storage:
Methane gas is expected to play an important role in the future of energy storage due to several factors:
- Renewable Methane: Methane gas can be produced from renewable sources such as agricultural waste, sewage, or landfill gas. This renewable methane can be used to produce electricity or heat, providing a sustainable energy storage solution.
- Green Hydrogen Production: Methane can be used as a feedstock to produce hydrogen through a process called steam methane reforming. This process produces hydrogen and carbon dioxide, which can be captured and stored, reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The hydrogen can then be used as a clean fuel for transportation, electricity generation, or industrial processes.
- Carbon Capture and Storage: Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is a process of capturing carbon dioxide emissions from power plants or industrial processes and storing them underground. Methane gas can be used as a carrier for carbon dioxide during CCS, making it an attractive option for reducing emissions from fossil fuel-based energy systems.
- Energy Storage for Transportation: Methane gas can be used as fuel for transportation, particularly in heavy-duty vehicles such as trucks and buses. The use of methane gas as a transportation fuel reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional fossil fuels, making it an attractive option for reducing emissions in the transportation sector.
- Hybrid Energy Storage Systems: Methane gas can be used in hybrid energy storage systems that combine different energy storage technologies such as batteries and hydrogen fuel cells. These systems can provide a more reliable and efficient energy storage solution than using a single technology.
Overall, the future of methane gas as an energy storage medium looks promising. As the world transitions to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future, methane gas is expected to play an increasingly important role in energy storage and generation. The development of renewable methane, green hydrogen production, carbon capture and storage, energy storage for transportation, and hybrid energy storage systems are all opportunities for the growth and adoption of methane gas as an energy storage medium.
