Green Energy vs Clean Energy vs Renewable Energy
Introduction
Green energy, clean energy, and renewable energy are all terms that describe different types of energy sources that are used to power our world. With growing concerns about climate change, air pollution, and energy security, these terms have become increasingly important as we search for alternative ways to generate electricity, heat our homes, and fuel our vehicles.
Renewable energy refers to energy sources that are naturally replenished and can be used indefinitely, such as solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass. These sources of energy have a minimal impact on the environment and are seen as a way to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels, which are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions.
Clean energy, on the other hand, refers to any form of energy that produces little or no pollution. This includes renewable energy sources like solar and wind, but also nuclear energy, which produces no greenhouse gas emissions but has other environmental concerns like waste disposal and safety.
Green energy is a subset of renewable energy that specifically refers to energy sources that have a minimal impact on the environment. This can include solar, wind, and hydro, as well as other renewable sources that have a low carbon footprint and are sustainable over the long term.
All three terms are important in the context of sustainable energy, as we seek to transition away from fossil fuels and toward cleaner, more sustainable forms of energy. By understanding the differences between these terms, we can make more informed decisions about the types of energy we use and the impact they have on the environment.
Green energy, clean energy, and renewable energy are often used interchangeably, but they have slightly different meanings:
Green energy:
Green energy refers to energy sources that have a minimal impact on the environment. This includes renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy. These sources of energy are considered green because they produce little or no pollution and have a much lower impact on the environment than fossil fuels.
Green energy is becoming increasingly important as we search for alternatives to fossil fuels, which are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. By transitioning to green energy sources, we can reduce our carbon footprint and help to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
In addition to their environmental benefits, green energy sources also have economic benefits. As the cost of renewable energy technologies continues to decline, it is becoming increasingly competitive with fossil fuels. This means that investing in green energy can create new jobs and boost local economies.
Overall, green energy is a critical component of a sustainable energy future. By transitioning to renewable energy sources and reducing our dependence on fossil fuels, we can help to create a more sustainable, equitable, and prosperous future for all.
Clean energy
Clean energy refers to any form of energy that produces little or no pollution. This includes renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy, as well as non-renewable sources such as nuclear energy.
The goal of clean energy is to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels, which are major contributors to air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and climate change. By transitioning to clean energy sources, we can reduce our carbon footprint and improve air quality, which can have significant public health benefits.
Clean energy sources like solar and wind are becoming increasingly competitive with fossil fuels, and in some cases, they are now cheaper than traditional energy sources. This has led to a growing demand for clean energy, as businesses and individuals seek to reduce their carbon footprint and take advantage of cost savings.
One of the challenges of clean energy is the issue of intermittency. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are dependent on weather conditions, which can vary widely from day to day and from region to region. To address this challenge, there is a growing need for energy storage technologies that can store excess energy during times of high production and release it when demand is high.
Despite these challenges, clean energy is seen as a critical component of a sustainable energy future. By transitioning to clean energy sources and reducing our dependence on fossil fuels, we can help to create a cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable future for all.
Renewable energy
Renewable energy refers to any form of energy that is derived from naturally replenishing sources, such as the sun, wind, water, and geothermal heat. These sources of energy are considered renewable because they can be replenished naturally and sustainably over time, unlike fossil fuels which are finite and non-renewable.
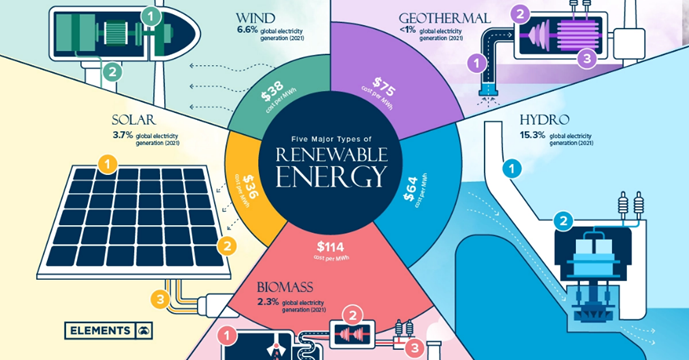
Renewable energy sources include solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass energy. Solar energy is derived from the sun’s rays, which can be converted into electricity through the use of solar panels. Wind energy is generated by wind turbines that convert the kinetic energy of wind into electricity. Hydroelectric power is generated by harnessing the power of flowing water, such as in rivers or dams. Geothermal energy is derived from the heat of the earth’s core, which can be used for heating and electricity generation. Biomass energy is generated from organic matter, such as wood chips, crop residues, and municipal waste.
The benefits of renewable energy are many. Renewable energy sources are clean and produce little or no pollution, making them a much more sustainable and environmentally-friendly alternative to fossil fuels. They also have the potential to be much more cost-effective over time, as the cost of renewable energy technologies continues to decline and become more competitive with traditional energy sources.
One of the main challenges with renewable energy is the issue of intermittency. Unlike fossil fuels, renewable energy sources are dependent on weather conditions and may not be available at all times. To address this challenge, there is a growing need for energy storage technologies that can store excess energy during times of high production and release it when demand is high.
Despite these challenges, renewable energy is seen as a critical component of a sustainable energy future. By transitioning to renewable energy sources and reducing our dependence on fossil fuels, we can help to create a cleaner, more sustainable, and more equitable energy future for all.
In summary, green energy and clean energy are often used to describe the environmental impact of energy sources, while renewable energy refers to the ability of the energy source to be replenished naturally over time. All three terms generally refer to sustainable energy sources that have a minimal impact on the environment.
Green Energy:
Green energy is that which comes from natural sources, such as the sun. Clean energy is those types that do not release pollutants into the air, and renewable energy comes from sources that are constantly being replenished, such as hydro power, wind power, or solar energy.
Green energy often derives from renewable energy sources such as solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, biomass, and hydroelectric power.
Each of these technologies generates energy in a unique manner, whether by capturing energy from the sun, as with solar panels, or by using wind turbines or the flow of water.
Green energy comes from resources that don’t pollute the environment, like fossil fuels. This means that the renewable energy industry doesn’t use only green sources. For example, making electricity by burning organic matter from sustainable forests may be renewable, but that doesn’t mean it’s green because the burning process itself releases CO2.
Green energy sources are usually replenished by nature, while fossil fuels like coal and natural gas can take millions of years to form. Green sources also try to stay away from mining and drilling, which can hurt ecosystems.
Wind power, solar power, and hydroelectric power are the main ones (including tidal energy, which uses ocean energy from the tides in the sea). Solar and wind power can be made in small amounts at people’s homes, or they can be made in large amounts on an industrial scale.
Here are the six most common types: (i) Solar power (ii) Wind Power (iii) Hydropower (iv) Geothermal Energy (v) Biomass and (vi) Biofuels
Clean Energy:
Renewable energy is often seen as being the same, but there is still some debate around this. For example, can a hydroelectric dam that may divert waterways and impact the local environment really be called ‘green?’
Clean energy comes from sources that don’t put pollution into the air. Green energy, on the other hand, comes from natural sources. Even though these two kinds of energy are often thought to be the same, there is a small difference between them.
The power that comes from sources that are always being refilled is called “renewable energy.” These sources of energy, like wind and solar power, will never run out, unlike fossil fuels and gas.

But even though most green energy sources are renewable, not all renewable energy sources are seen as green.
For example, hydropower is a renewable resource, but some people would argue that it is not green because the building of hydro dams can damage the environment by cutting down trees and making it more industrial.
The best clean energy mix is made up of both green energy and renewable energy, like solar and wind power.
A simple way to remember the differences between these types of energy is:
- Clean energy = clean air
- Green energy = natural sources
- Renewable energy = recyclable sources
Clean energy is a way to make electricity without harming the environment, like by letting out greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide. A lot of clean energy is also renewable, like wind power, some types of hydropower, and solar power.
As part of a global energy future, the most important thing about clean energy is that it is good for the environment. Clean, renewable resources help keep the world’s natural resources in good shape, and they also lower the risk of environmental disasters like fuel spills and problems caused by natural gas leaks.
With fuel diversification, where different power plants use different energy sources, it is possible to create reliable power supplies to make sure there is enough energy to meet our needs and improve energy security.
Clean energy helps the environment and the economy in many ways, like cutting down on air pollution. A variety of clean energy sources also makes it less necessary to import fuels (and the associated financial and environmental costs this incurs).
Renewable, clean energy also saves money because there’s no need to extract and transport fuels, like oil or coal, and the resources naturally replenish themselves, so there’s no need to do either.
A clean energy mix also helps the economy by creating jobs to develop, make, and put in place the clean energy resources of the future.
Renewable
However, a source such as wind power is renewable, green, and clean – since it comes from an environmentally friendly, self-replenishing, and non-polluting source.
Renewable energy is growing quickly because new ideas are bringing down costs and making it possible to start living up to the promise of a clean energy future. Solar and wind power in the United States are breaking records and are being added to the national electricity grid without making it less reliable.
This means that renewables are replacing “dirty” fossil fuels in the power sector more and more. This means that carbon and other types of pollution are being released into the air less. But not all “renewable” sources of energy are good for the environment.
When wildlife, climate change, and other issues are taken into account, biomass and large hydroelectric dams create hard trade-offs. Here’s what you should know about the different types of renewable energy sources and how you can use these new technologies in your own home.
Renewable energy, which is also called “clean energy,” comes from natural sources or processes that keep making more energy. For example, the sun and wind will always shine and blow, even though when they are available depends on time and weather.
People often think of renewable energy as a new technology, but using the power of nature to heat, move, light, and do other things has been done for a long time.
The wind has helped sail ships across the seas and powered windmills to grind grain. During the day, the sun has kept people warm and helped people start fires that will last until the evening. But in the past 500 years or so, people have turned more and more to cheaper, dirtier energy sources, like coal and fracked gas, because they are less expensive.
Green Energy vs Clean Energy vs Renewable Energy difference
a table that summarizes the main differences between green energy, clean energy, and renewable energy:
| Energy Source | Renewable? | Clean? | Green? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Wind | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Hydroelectric | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Geothermal | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Biomass | Yes | Yes | Sometimes |
| Nuclear | No | Yes | No |
| Fossil Fuels | No | No | No |
Renewable energy sources are those that are naturally replenished and can be used indefinitely. All the energy sources listed in the table except for nuclear and fossil fuels are renewable.
Clean energy sources are those that produce little or no pollution. This includes renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro, as well as nuclear energy, which produces no greenhouse gas emissions but has other environmental concerns like waste disposal and safety.
Green energy sources are a subset of renewable energy sources that have a minimal impact on the environment. Solar, wind, and hydroelectric energy are generally considered green energy sources. Biomass can also be considered green energy, but only if it is produced sustainably and does not contribute to deforestation or other environmental damage.
In summary, renewable energy sources are naturally replenished and can be used indefinitely, clean energy sources produce little or no pollution, and green energy sources have a minimal impact on the environment.

