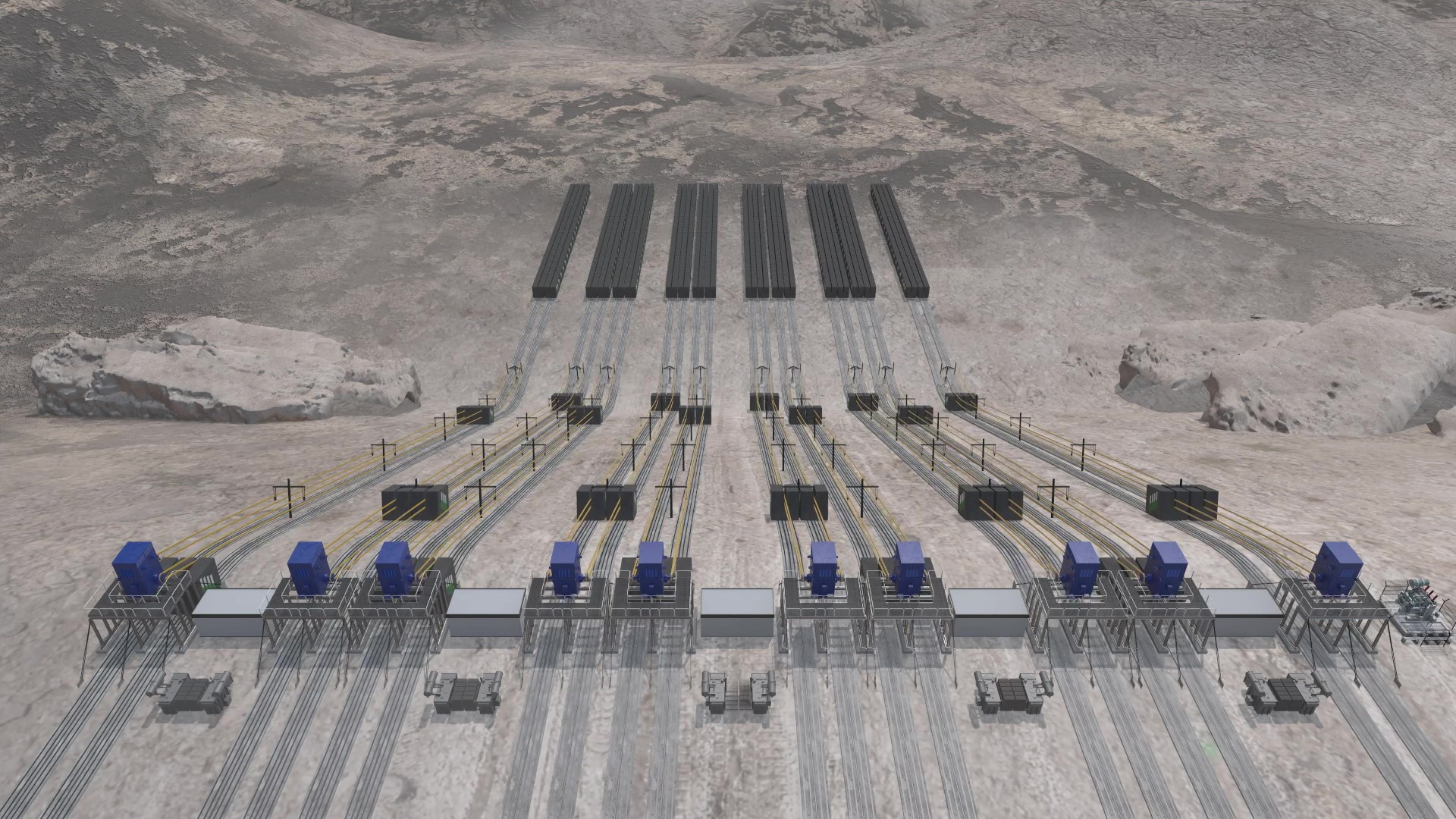
Advanced Rail Energy Storage possibility
Introduction
Advanced Rail Energy Storage (ARES) is a unique technology that has the potential to revolutionize energy storage. It works by using the potential energy of a mass of heavy railcars that are lifted to a higher elevation when surplus electricity is available, and then the railcars are allowed to roll down to generate electricity when needed. This system can provide a flexible and scalable solution for energy storage that can help to address some of the challenges of integrating renewable energy sources into the grid.
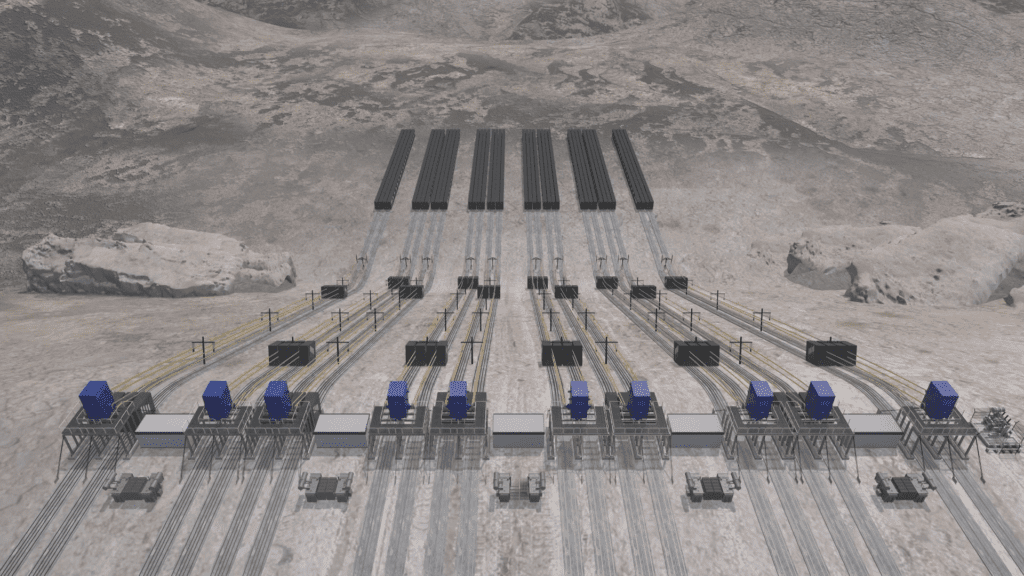
One of the key advantages of ARES technology is its scalability. The system can be designed to store any amount of energy, from a few megawatt-hours to hundreds of megawatt-hours. This means that ARES can be used to provide energy storage solutions for a wide range of applications, from small-scale residential systems to large-scale grid storage systems.
Another advantage of ARES technology is its ability to provide fast response times. Unlike some other energy storage technologies that can take several minutes to respond to changes in demand, ARES can respond in seconds. This makes it an ideal solution for balancing the grid and ensuring grid stability.
In terms of companies in America that are involved in ARES, one of the most prominent is ARES North America. ARES North America is based in Santa Barbara, California, and has developed a proprietary technology for using rail energy storage to provide grid-scale energy storage services. The company has already completed several projects and has demonstrated the effectiveness and reliability of its technology.
One of the notable ARES projects completed by ARES North America was the Pahrump Valley Energy Storage Project in Nevada. This project involved the construction of a 50 MW / 200 MWh ARES system that used a 9-mile-long track to store and generate energy. The system was designed to provide grid-scale energy storage services to the California Independent System Operator (CAISO), which manages the majority of the California grid.
Another company that has shown interest in ARES technology is BNSF Railway. BNSF Railway is one of the largest freight rail networks in North America, and it has partnered with ARES North America to explore the potential of using its rail network to provide energy storage services. BNSF Railway has extensive rail infrastructure that could be used to support ARES systems, and the partnership could lead to the development of new energy storage projects that use rail-based energy storage.
Other companies that are exploring the potential of ARES technology include Gravity Power, LAZARUS Energy, and Energy Vault. Gravity Power is based in Santa Barbara, California, and is developing a gravity-based energy storage system using ARES technology. The system works by lifting and dropping weights to generate electricity, and it has the potential to provide grid-scale energy storage services. LAZARUS Energy is based in Denver, Colorado, and is developing a rail-based energy storage system using ARES technology. The company has developed a unique system that uses linear motors to move the railcars up and down the track, which allows for greater control over the energy storage process. Energy Vault is based in Lugano, Switzerland, but has a presence in the United States, and is developing a gravity-based energy storage system using concrete blocks. The company has developed a unique system that uses a tower of concrete blocks that are lifted and dropped to generate electricity.
A list of Companies are working on Advanced Rail Energy Storage systems

There are several companies in America that are working on Advanced Rail Energy Storage (ARES) technology. Here is a list of some of the companies that are currently involved in developing, deploying, or promoting ARES systems:
- ARES North America – ARES North America is a company that specializes in developing and deploying ARES technology. The company has partnered with BNSF Railway to develop several ARES projects in the US.
- Gravity Power LLC – Gravity Power LLC is a company that is developing a variant of ARES technology known as Gravity Power Module (GPM). GPM uses a similar concept to ARES, but instead of using rail cars, it relies on gravity to store and generate energy.
- American Rail Energy – American Rail Energy is a company that is developing ARES systems for energy storage and grid stabilization. The company is based in California and has several ARES projects in development.
- Pacific Gas and Electric (PG&E) – PG&E is a utility company that is exploring the potential of ARES technology for energy storage and grid stabilization. The company has partnered with ARES North America to develop an ARES project in California.
- E.ON Climate & Renewables – E.ON is a renewable energy company that is exploring the potential of ARES technology for grid stabilization. The company has several ARES projects in development, including a project in Texas.
- Northwest Power and Conservation Council – The Northwest Power and Conservation Council is a regional planning agency that is exploring the potential of ARES technology for energy storage in the Pacific Northwest. The agency is conducting a feasibility study to determine the viability of ARES systems in the region.
- The Energy Authority – The Energy Authority is a non-profit energy consulting firm that is exploring the potential of ARES technology for energy storage and grid stabilization. The firm has partnered with American Rail Energy to develop an ARES project in California.
These are just a few of the companies that are working on Advanced Rail Energy Storage technology in America. As the technology continues to evolve and gain traction, we can expect to see more companies and organizations exploring the potential of ARES for energy storage and grid stabilization.
Overall, ARES technology has the potential to play an important role in the future of energy storage, and several companies in America are exploring its possibilities. With its scalability, fast response times, and flexible design, ARES technology could help to address some of the key challenges of integrating renewable energy sources into the grid. As more companies and organizations explore the potential of ARES technology, we are likely to see more projects and innovations that demonstrate the benefits of this exciting energy storage technology.
Future of Advanced Rail Energy Storage Systems in America
The future of Advanced Rail Energy Storage (ARES) in America looks promising. The technology offers several advantages that make it an attractive option for grid-scale energy storage. With the increasing deployment of renewable energy sources, the need for reliable energy storage solutions is growing, and ARES has the potential to play an important role in meeting this demand.

One of the key advantages of ARES is its scalability. The system can be designed to store any amount of energy, from a few megawatt-hours to hundreds of megawatt-hours. This means that ARES can be used to provide energy storage solutions for a wide range of applications, from small-scale residential systems to large-scale grid storage systems.
Another advantage of ARES is its fast response times. Unlike some other energy storage technologies that can take several minutes to respond to changes in demand, ARES can respond in seconds. This makes it an ideal solution for balancing the grid and ensuring grid stability.
In addition to these advantages, ARES is also a relatively low-cost energy storage solution. The technology is based on existing rail infrastructure, which reduces the cost of deployment. ARES also has a long lifespan and low maintenance requirements, which can further reduce the overall cost of ownership.
One of the challenges facing ARES is the need for suitable sites to build the system. ARES requires a steep incline to store and generate energy, which limits the potential locations where the technology can be deployed. However, there are many areas in America that have suitable topography, such as mountains and hills, which could be used to deploy ARES systems.
In terms of the future of ARES in America, there are several factors that could drive its adoption. These include:
- The increasing deployment of renewable energy sources is creating a growing demand for energy storage solutions.
- The need for grid stability and reliability, particularly as more intermittent renewable energy sources are integrated into the grid.
- The potential for ARES to provide grid-scale energy storage services that are low-cost and reliable.
- The partnership between ARES North America and BNSF Railway could lead to the development of new energy storage projects that use rail-based energy storage.
- The potential for ARES to be combined with other energy storage technologies, such as batteries and flywheels, to create hybrid energy storage solutions that offer even greater flexibility and scalability.
Overall, the future of ARES in America looks promising. With its scalability, fast response times, and low cost, ARES has the potential to play an important role in meeting the growing demand for reliable energy storage solutions. As more companies and organizations explore the potential of ARES technology, we are likely to see more projects and innovations that demonstrate the benefits of this exciting energy storage technology.
Present status of the ARES system in America

As of my knowledge cutoff in 2021, there were no commercially operational Advanced Rail Energy Storage (ARES) systems in America. However, there have been several ARES projects proposed and in development in different parts of the country.
ARES is a technology that uses excess energy from renewable sources, such as wind and solar, to drive heavy rail cars up a slope. When energy is needed, the cars are released and the kinetic energy is converted back into electricity. The technology has the potential to store large amounts of energy at a lower cost than other energy storage technologies.
One proposed project in California would use an ARES system to store renewable energy generated during the day and release it during peak demand periods. Another proposed project in Nevada would use an ARES system to store energy generated by a solar power plant.
Overall, while there are currently no operational ARES systems in America, there are ongoing efforts to develop and implement this technology as a means of energy storage and management.
Present status of the Advanced Rail Energy Storage (ARES) system in the rest of the world
The Advanced Rail Energy Storage (ARES) system is a novel technology for grid-scale energy storage that uses electric railcars to store energy. The system was initially developed by a California-based company called ARES North America, and it has garnered significant interest from researchers and policymakers around the world due to its potential to address the intermittency and variability of renewable energy sources.
While ARES has yet to be deployed on a large scale outside of the United States, there have been several pilot projects and feasibility studies in various countries. In Germany, a feasibility study was conducted in 2015 to assess the potential of ARES for energy storage in the railway system. The study concluded that ARES could be a promising technology for energy storage in railways, particularly for regenerative braking energy, which is currently wasted.
In Chile, a pilot project was launched in 2018 to test the feasibility of using ARES for grid-scale energy storage. The project involves building a 500-kilowatt ARES system on a hillside near the city of Arica, which will store excess solar energy during the day and release it during the night when demand is high. The project is expected to be operational in 2021.
In Japan, researchers at the University of Tokyo have proposed using ARES as a cost-effective alternative to lithium-ion batteries for grid-scale energy storage. The researchers claim that ARES has the potential to store energy at a lower cost and with a longer lifespan than current battery technologies. The proposal is currently being evaluated by the Japanese government.
In addition to these countries, there has been interesting in ARES from other countries, including India, Australia, and South Africa. In India, ARES technology has been tested on a small scale at the Indian Institute of Technology in Bombay, and there are plans to explore its potential for grid-scale energy storage in the future. In Australia, a consortium of researchers and industry partners is exploring the use of ARES for renewable energy integration in remote and off-grid areas. In South Africa, ARES technology has been proposed as a solution to address the country’s energy crisis and provide reliable and affordable energy storage.
Overall, while ARES is still in the early stages of development and deployment, there is growing interest in technology around the world. As renewable energy becomes increasingly important for global energy systems, ARES has the potential to play a key role in enabling the transition to a more sustainable and resilient energy future.
Future Business Opportunities on Advanced Rail Energy Storage (ARES)
There are several potential business opportunities that could arise from the development and deployment of Advanced Rail Energy Storage (ARES) systems. Here are a few possibilities:
- Energy storage project development: As interest in ARES grows, there may be opportunities for companies to develop and construct large-scale ARES projects for utilities and other customers.
- Operations and maintenance services: ARES systems require regular maintenance and monitoring to ensure optimal performance. Companies that specialize in these services could find new business opportunities as ARES becomes more widespread.
- Consulting and engineering services: Companies that offer consulting and engineering services related to renewable energy and energy storage could expand their offerings to include ARES.
- Equipment and materials supply: ARES systems require specialized equipment and materials, such as regenerative braking systems and high-capacity energy storage devices. Companies that supply these components could see increased demand as ARES becomes more prevalent.
- Transportation and logistics: ARES systems often require the transportation of heavy equipment and materials over long distances. Companies that specialize in transportation and logistics could find new business opportunities in this area.
- Research and development: There may be opportunities for companies to conduct research and development on new ARES technologies and applications, such as using ARES for electric vehicle charging or grid stabilization.
- Financing and investment: As ARES becomes more established, there may be opportunities for companies to invest in or finance ARES projects, either as direct investors or through partnerships with utilities and other stakeholders.
Overall, the potential business opportunities in Advanced Rail Energy Storage (ARES) are vast and varied, offering a wide range of possibilities for companies and entrepreneurs looking to enter the growing renewable energy market.
Top 10 books on Advanced Rail Energy Storage (ARES) system
- “The Advanced Rail Energy Storage System: A Potential Solution for Energy Storage” by Pengfei Wang and Lei Shi.
- “Advanced Rail Energy Storage (ARES): A New Approach to Energy Storage” by Christopher B. Durrant and Anton E. Bowden.
- “Energy Storage: A Vital Element in Today’s Electricity Industry” by David A. Wood.
- “Grid-Scale Energy Storage: The Case for Pumped Hydro and Advanced Rail Energy Storage” by John P. Wagner and Bryan Palmintier.
- “Renewable Energy Integration: Practical Management of Variability, Uncertainty, and Flexibility in Power Grids” by Lawrence E. Jones.
- “Energy Storage: Technologies and Applications” by Rebecca Hernandez and Sara Bergan.
- “Introduction to Energy Storage: Materials, System, and Applications” by Chunlei Guo and Weishan Li.
- “Energy Storage for Power Systems” by Hong Chen and Qiuwei Wu.
- “Energy Storage for Sustainable Microgrid” by Hongjie Jia, Wenxin Liu, and Yunhang Wu.
- “Renewable Energy Integration: Challenges and Solutions” edited by Yuanzhang Sun and Yaochu Jin.